Dornier Do 31 Video - Picture
|
|
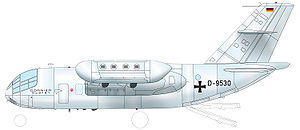
Dornier Do 31
Dornier Do 31

Role: VTOL transport
Manufacturer: Dornier Flugzeugwerke
First flight: 10 February 1967
Status: Project cancelled April 1970
Primary user: Luftwaffe
Number built: 3
The Dornier Do 31 was a West German experimental VTOL jet transport built by Dornier. The Do 31 was designed to meet a NATO specification (BMR-4) for a tactical support aircraft for the EWR VJ 101 VTOL strike aircraft designed under the NATO contract of BMR-3. The project was cancelled in 1970 due to high costs, technical problems and a change of requirement.
Design and development
In the early 1960s, the Luftwaffe became increasingly concerned that their airfields were vulnerable to air attack from Eastern Bloc forces and actively researched the possibility of dispersed operations which included flying from Autobahnen but required aircraft with STOVL capabilities. Part of these trials involved Luftwaffe F-104 Starfighters being rocket launched from stationary ramps in what became known as the ZELL program. The Starfighters were to be recovered to short strips using aircraft carrier-type arresting gear. The Do 31 was intended to use the same strips as forward operating bases.
When the high cost, technical and logistical difficulties were realised the Luftwaffe ceased trials involving VTOL aircraft such as the Do 31, VJ101 and the later VFW VAK 191B which resulted in the cancellation of these projects and further use of these aircraft was limited to research purposes only.
Initial designs incorporated a Bristol Pegasus vectored-thrust turbofan in each of the two inboard nacelles and four Rolls-Royce RB162 lift engines in each of the outer nacelles. It was planned to dispense with the outer nacelles and their engines when larger RB153 turbofans (of approximately 5,000 lbf (22 kN) thrust) became available. By mounting the engines in pods, the fuselage could provide a capacious hold with a rear loading ramp.
In all, three test articles were built, these being E1, E2 and E3 - the "E" indicating Experimentell (Experimental). E1 was powered only by the Pegasus engines, and was designed to test horizontal flight. E2 was a static test airframe, and did not fly. E3 had both Pegasus and RB162 lift engines installed, and was designed to test the vertical flight mode. The first prototype (E1) first flew on 10 February 1967 with just the two Pegasus engines. The third prototype (E3) flew in July 1967 with all ten engines fitted. The first hovering flight took place on 22 November 1967. Full forward and backward transitions were made in December 1967.
The Do 31 established several Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI) world records during its ferry flight to the 1969 Paris Air Show. It was the first, and so far only, vertical take-off jet transport ever built. The project was cancelled in April 1970, although it made its final public flight on 4 May 1970 during the ILA in Hanover. One of the factors that led to the cancellation was the large drag and weight of the lift engine pods which reduced the useful payload and range compared to conventional transport aircraft.
Survivors

Picture - Do 31 E3 on display
Both flying prototypes have been preserved in Germany, the fate and current location of the non-flying test bed (E2) is not known.
Dornier Do 31 E1, D-9530, is preserved and displayed at the Dornier Museum in Friedrichshafen.
Dornier Do 31 E3, D-9531, was initially put into storage at Oberpfaffenhofen and is on display at the Deutsches Museum Flugwerft Schleissheim at Oberschleissheim near Munich
Operators
Germany
Luftwaffe
Specifications (Do 31E)

Picture - Flight deck of the Do 31
Data from "The Observers Book of Aircraft"
General characteristics
Crew: 2
Capacity: 36 troops or 24 casualty stretchers
Length: 20.53 m (67 ft 4 in)
Wingspan: 18 m (59 ft 3 in)
Height: 8.53 m (28 ft)
Wing area: 57 m² (613.56 ft²)
Loaded weight: 22,453 kg (49,500 lb)
Useful load: 3,500 kg (7,715 lb)
Max takeoff weight: 27,422 kg (60,500 lb)
Powerplant:
2x— Rolls-Royce Pegasus BE.53/2 turbofan, 68.95 kN (15,500 lbf) each
8x— Rolls-Royce RB162-4D Vertically mounted turbojet lift engines, 19.57 kN (4,400 lbf) each
Performance
Maximum speed: 730 km/h (452 mph)
Cruise speed: 650 km/h (404 mph)
Range: 1,800 km (1,120 mi) with maximum payload
Service ceiling: 10,700 m (35,100 ft)
Rate of climb: 19.2 m/s (3,780 ft/min) -using Pegasus engines only
Comparable aircraft
Armstrong Whitworth AW.681
Bibliography
Green, William. The Observer's Book of Aircraft. London. Frederick Warne & Co. Ltd., 1968.
Jackson, Paul A. German Military Aviation 1956-1976. Hinckley, Leicestershire, UK: Midland Counties Publications, 1976. ISBN 0-904597-03-2.
Dornier Do 31 Pictures
More aircraft.
Source: WikiPedia