Northrop A-17 Video - Picture

|
|
Northrop A-17
A-17 / Nomad

Picture - Northrop A-17
Role: Ground attack
Manufacturer: Northrop
Designed by: Jack Northrop
Introduced: 1935
Primaryusers: United States Army Air Corps
Swedish Air Force
Royal Canadian Air Force
South African Air Force
Number built: 446
Developed from: Northrop Gamma
The Northrop A-17, a development of the Northrop Gamma 2F was a two seat, single engine, monoplane, attack bomber built in 1935 by the Northrop Corporation for the US Army Air Corps.
Development and design
The Northrop Gamma 2F was an attack bomber derivative of the Northrop Gamma transport aircraft, developed in parallel with the Northrop Gamma 2C, (of which one was built, designated the YA-13 and XA-16. The Gamma 2F had a revised tail, cockpit canopy and wing flaps compared with the Gamma 2C, and was fitted with a new semi-retractable undercarriage. It was delivered to the United States Army Air Corps for tests on 6 October 1934, and after modification, including fitting with a conventional fixed undercarriage, was accepted by the Air Corps. 110 aircraft were ordered as the A-17 in 1935.
The resulting A-17 was equipped with perforated flaps, had fixed landing gear with partial fairing. It was fitted with an internal fuselage bomb bay that carried fragmentation bombs and well as external bomb racks.
Northrop developed a new undercarriage, this time completely retractable, producing the A-17A variant. This version was again purchased by the Army Air Corps, who placed orders for 129 aircraft. By the time these were delivered, the Northrop Corporation had been taken over by Douglas Aircraft Company, export models being known as the Douglas Model 8.
Operational history

Picture - A-17A cockpit
The A-17 entered service in February 1936, and proved a reliable and popular aircraft. However, in 1938, the Air Corps decided that attack aircraft should be multi-engined, rendering the A-17 surplus to requirements.
In June 1940, 93 ex-USAAC aircraft were purchased by France, and refurbished by Douglas , including being given new engines. Not having been delivered before the fall of France, 61 were taken over by the British Purchasing Commission for the RAF and given the name Nomad. They were assessed as being obsolete and sent to South Africa for use as trainers. The remaining thirty two aircraft from the French order were transferred to Canada, where they were also used as advanced trainers.
The last remaining A-17s, used as utility aircraft, were retired from USAAF service in 1944.
Variants

Picture - A-17A 36-0207
A-17 Initial production for USAAC. Fixed undercarriage, powered by 750hp (560kW) Pratt & Whitney R-1535-11 Twin Wasp Jr engine. 110 built. A-17A Revised version for USAAC with retractable undercarriage and 825hp (615kW) R-1535-13 engine. 129 built. A-17AS Three seat staff transport version for USAAC. Powered by Pratt & Whitney R-1340 Wasp engine. Two built. Model 8A-1 Export version for Sweden. Fixed undercarriage. Two Douglas built prototypes (Swedish designation B 5A), followed by 63 licensed built (by ASJA) B 5B aircraft powered by 920hp (686kW) Bristol Mercury XXIV engine. 31 similar B 5C built by SAAB. Model 8A-2 Version for Argentina. Fitted with fixed undercarriage, ventral gun position and powered by 840hp (626kW) Wright R-1820-G3 Cyclone. 30 built. Model 8A-3N Version of A-17A for Netherlands. Powered by 1,100hp (820kW) Pratt & Whitney R-1830 Twin Wasp engine. 18 built. Model 8A-3P Version of A-17A for Peru. Powered by 1,000hp (746kW) R-1820 engine. Ten built. Model 8A-4 Version for Iraq, powered by a 1,000hp (746kW) R-1820-G103 engine. 15 built. Model 8A-5N Version for Norway, powered by 1,200hp (895kW) R-1830 engine. 36 built. Later impressed into USAAF service as Douglas A-33.
Survivors
A-17A 36-0207 c/n 234, ex-3rd Attack Group (Barksdale Field), On display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force in Dayton, Ohio
8A-3P 4??, ex-31 Escuadrx³n de Ataque y Reconocimiento. On display at the FAP museum, Las Palmas Peruvian Air Force Base.
Operators
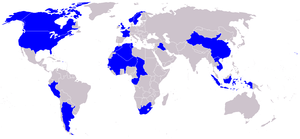
Picture - Operators of the A-17
Argentina Argentina purchased 30 Model 8A-2s in 1937 and received them between February and March 1938. Their serial numbers were between 348 and 377. These remained in front line service until replaced by the I.Ae. 24 Calquin, continuing in service as trainers and reconnaissance aircraft until their last flight in 1954.
Grupo "A" de la Escuela de Aplicacix³n de Aviacix³n based at BAM El Palomar
Regimiento Aéreo Nº3 (Air Regiment No.3) de Bombardeo Liviano (Light Bombing) based at BAM El Plumerillo
Canada
Royal Canadian Air Force received 32 ex-French aircraft serialled 3490 to 3521 - designated Nomad - all assigned to 3rd Training Command.
France
French Air Force ordered 93 aircraft but when France fell all were delivered to Great Britain and Canada.
Iraq Iraq purchased 15 Model 8A-4s, in 1940. They were destroyed in the Anglo-Iraqi War in 1941. Netherlands The Netherlands, in urgent need of modern combat aircraft, placed an order for 18 Model 8A-3Ns in 1939, with all being delivered by the end of the year. Used in a fighter role for which they were unsuited, the majority were destroyed by Luftwaffe attacks on 10 May 1940, the first day of the German invasion.. In his 1975 book on Dutch aviation history Vermetele vliegende Hollanders (Daring flying Dutchmen), Dutch aviation historian and illustrator Thijs Postma lists these planes as Douglas 8A. Norway Norway ordered 36 Model 8A-5Ns in 1940. These were not ready by the time of the German Invasion of Norway and were diverted to Norwegian Training unit in Canada, which became known as Little Norway. Norway decided to sell 18 of these aircraft as surplus to Peru, but these were embargoed by the United States, who requisitioned the aircraft, using them as trainers, designating them the A-33. Norway sold their surviving aircraft to Peru in 1943. Peru Peru ordered 10 Model 8A-3Ps, these being delivered from 1938 onwards. These aircraft were used in combat by Peru in the Ecuadorian-Peruvian war of July 1941. The survivors of these aircraft were supplemented by 13 Model 8A-5s from Norway, delivered via the United States in 1943. These remained in service until 1958. South Africa
South African Air Force received 57 aircraft from Great Britain designated Nomad I.
Sweden
Swedish Air Force - Sweden purchased a licence for production of a Mercury powered version, building 63 B 5Bs and 31 B5Cs, production taking place from 1938 to 1941. They were replaced in service by SAAB 17s from 1944. The Swedish version was used as dive bomber and as such it featured prominently in the 1941 film 'Fx¶rsta Divisionen'.
United Kingdom
Royal Air Force received 61 ex-French aircraft redesignated as Nomad I but 57 were handed over to South Africa. British Nomads were serialed AS440 to AS462, AS958 to AS976 and AW420 to AW438.
United States
United States Army Air Corps received 110 A-17s and 129 A-17As
3d Attack Group based at Barksdale Field
17th Attack Group based at March Field
16th Pursuit Group based at Albrook Field
74th Attack Squadron
General Headquarters Air Force operated several aircraft for use as staff transports.
Specifications (A-17)
Data from McDonnell Douglas Aircraft since 1920
General characteristics
Crew: two (pilot and gunner)
Length: 31 ft 8â
in (9.67 m)
Wingspan: 47 ft 8½ in (14.54 m)
Height: 11 ft 10½ in (3.62 m)
Wing area: 363 sq ft (33.7m²)
Empty weight: 4,874 lb (2,211 kg)
Loaded weight: 7,337 lb (3,328 kg)
Powerplant: 1x Pratt & Whitney R-1535-11 Twin Wasp Jr two-row air-cooled radial engine, 750 hp (560 kW)
Performance
Maximum speed: 206 mph (179 knots, 332 km/h)
Cruise speed: 170 mph (149 knots, 274 km/h)
Range: 650 mi (565 nmi, 1,046 km)
Service ceiling: 19,400 ft (5,915 m)
Rate of climb: 1,350 ft/min (6.9 m/s)
Armament
4 x 0.3 in (7.62 mm) fixed forward M1919 Browning machine guns
1 x 0.3 in (7.62 mm) trainable rear machine gun
Internal bay for bombs
External wing bomb racks (total bomb load 1,200 lb/544 kg)
1939 Crash
Lick Observatory
Related development
Northrop Gamma
Northrop YA-13
Northrop BT
Douglas A-33
Comparable aircraft
Blackburn Skua
Fairey Battle
Bibliography
Donald, David (ed). American Warplanes of World War II. London:Aerospace. 1995. ISBN 1 874023 72 7.
Francillon, René J. McDonnell Douglas Aircraft since 1920. London:Putanm, 1979. ISBN 0-370-00050-1.
Pelletier, Alain J. "Northrop's Connection: The unsung A-17 attack aircraft and its legacy - Part 1". Air Enthusiast No 75, May - June 1998. Stamford, Lincolnshire: Key Publishing. Page 62-67. ISSN 0143 5490.
Pelletier, Alain J. "Northrop's Connection: The unsung A-17 attack aircraft and its legacy - Part 2". Air Enthusiast No 77, September/October 1998. Stamford, Lincolnshire: Key Publishing. Page 2-15. ISSN 0143 5490.
Widfeldt, Bo and Hall, x
ke. B 5 Stx¶rtbombepoken (in Swedish). Nx¤ssjx¶, Sweden: Air Historic Research AB U.B., 2000. ISBN 91-9716-057-1.
Sergio Bontti. Serie Fuerza Aérea Argentina #8 Northrop 8A-2. Jorge Nux±ez Padin (editor) October 2003.
Living Warbirds: The best warbirds DVD series.
Source: WikiPedia