North American FJ-2/-3 Fury Video - Profiles in Aviation - The FJ-3 Fury
|
|
|
|
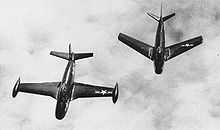
 Picture: USMC FJ-3Ms of VMF-235 in September 1957
Picture: USMC FJ-3Ms of VMF-235 in September 1957
Role - Fighter aircraft
National origin - United States
Manufacturer - North American Aviation
First flight - 27 December 1951
Introduced - 1954
Retired - early 1960s
Primary users - United States Navy
United States Marine Corps
Number built - 741
Developed from - F-86E Sabre
Developed into - FJ-4 Fury
The North American FJ-2/-3 Fury were a series of swept-wing carrier-capable fighters for the United States Navy and Marine Corps. Based on the United States Air Force's F-86 Sabre, these aircraft featured folding wings, and a longer nose landing strut designed to both increase angle of attack upon launch and to absorb the shock of hard landings on an aircraft carrier deck. Although sharing a U.S. Navy designation with its distant predecessor, the straight-winged FJ-1 Fury, the FJ-2/-3 were wholly different aircraft. The FJ-4 Fury was a complete stuctural redesign of the FJ-3.
Design and development
FJ-2
By 1951, the Navy's existing straight-wing fighters were much inferior in performance to the swept-wing Soviet MiG-15 then operating in the Korean War; the swept-wing fighters in the Navy's development pipeline, including the F7U Cutlass and F9F Cougar were not yet ready for deployment.
As an interim measure, the Navy's Bureau of Aeronautics ordered a direct development of the swept-wing F-86E Sabres as the FJ-2. As the F-86 had not been designed to be carrier-capable, this involved some risk, but Navy pilots had observed that the F-86A actually had a lower landing speed than the F9F Panther. The urgency behind the program was such that 300 (later reduced to 200) FJ-2 fighters were ordered before the prototypes had flown.
 Picture: FJ-1 and FJ-2 in 1952
Picture: FJ-1 and FJ-2 in 1952
The first prototype to fly was actually the third aircraft ordered: Designated XFJ-2B and first flown on 27 December 1951, it differed only from a standard F-86E-10 in its armament, having four 20-mm Colt Mk 12 cannon instead of the six Colt-Browning M3 .50 machine guns of the Sabre. The second and third aircraft to fly were designated XFJ-2 and lacked armament, but were modified to be carrier-capable: They had an arrester hook and a longer nosewheel leg to increase angle of attack at take-off and landing, and catapult fittings. In August 1952 carrier trials were flown on the USS Midway, followed by carrier qualification trials on the USS Coral Sea in October-December 1952. Results were less than satisfactory. Low-speed handling was considered poor, and the arrester hook and lose gear leg were insufficiently strong.
The first production aircraft flew on 22 November 1952. This FJ-2 incorporated further modifications for carrier operations: The track of the main landing gear was widened by eight inches, the outer wing panels folded upward, and the windscreen was modified to give the pilot a better view during approach. The FJ-2 also featured an all-moving "flying tail" without dihedral. Because of problems experienced during launches with steam catapults, a number of FJ-2 later received a stronger nosewheel strut. Outwardly, the FJ-2 was hard to distinguish from an F-86, apart from Navy paint and the gun muzzles of the 20-mm cannon. The engine was the General Electric J47-GE-2, a navalized version of the J47-GE-27 used in the F-86F. The naval modifications of the FJ-2 had increased weight by about 500 kg over the F-86F, but unfortunately had not succeeded in delivering a fully carrier-capable fighter. A decision had already been made to give it to land-based squadrons of the US Marine Corps.
Construction was slowed due to demand for the F-86 in Korea; the FJ-2 was not produced in large numbers until after that conflict had concluded. Only seven aircraft had been delivered by then end of 1953, and it was January 1954 before the first aircraft was delivered to a Marine squadron, VMF-122. The Navy preferred the lighter F9F Cougar due to its superior slow-speed performance for carrier operations, and the 200 FJ-2 models built were delivered to the United States Marine Corps. The Marines did make several cruises aboard carriers and tried to solve the type's carrier handling problems, but the FJ-2 was never really satisfactory. In 1956, the FJ-2 already disappeared from front-line service, and reserve units retired it in 1957.
FJ-3
 Picture: 4 FJ-3 Fury fighter-bombers of VF-33 and an AD-6 of VA-25 on the deck of the USS Intrepid in the North Atlantic in 1957.
Picture: 4 FJ-3 Fury fighter-bombers of VF-33 and an AD-6 of VA-25 on the deck of the USS Intrepid in the North Atlantic in 1957.
 Picture: A Fury displayed on the flight deck of the USS Intrepid museum ship.
Picture: A Fury displayed on the flight deck of the USS Intrepid museum ship.
Even while development of the FJ-2 was ongoing, the development was planned of a version powered by the Wright J65, a license-built version of the British Armstrong Siddeley Sapphire turbojet. The Sapphire promised to deliver 28% more thrust than the J47, for little gain in weight. The new version was designated FJ-3, and an order for 389 aircraft was placed in March 1952.
To test the new engine a single FJ-2, BuNo 131931, was modified, but the first true production FJ-3 flew in July 1953. The only externally visible change required by the new engine was a deeper intake to accommodate the larger mass flow. Early FJ-3s had the same wing as the FJ-2, but from 1955 onwards the FJ-3 was built with a so-called "6-3" wing, with a leading edge that was extended 6 inches at the root and 3 inches at the tip. This modification, first introduced on the F-86F, enhanced manoeuverability at the price of an small increase in landing speed because the leading edge slats were deleted. The version introduced on the FJ-3 was different from that fitted to the F-86F, as camber was applied to the underside of the leading edge to improve low-speed handling. On the FJ-3, the new wing leading edges also held extra fuel. From the 345th aircraft onwards, the wings were provided with four stations for external loads, up to 1000 lb on the inboard stations and 500lb on the outboard stations.
Deliveries began in September 1954, and the FJ-3 joined the fleet in May 1955. An FJ-3 was the first fighter to land aboard the new supercarrier USS Forrestal in 1956. Problems were encountered with the J65 engine, including failures of its lubrication system under the acceleration of launch or during manoeuvres, and failures of the turbine blades. Nevertheless the Navy was more satisfied with the FJ-3 than it had been with the FJ-2, and in March 1954 it ordered an additional 149 aircraft. Because of its more powerful engine, the FJ-3 was superior to most models of the F-86, except the F-86H. A total of 538 FJ-3s were built. Of these 194 were modified to FJ-3Ms with the ability to carry AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missiles. Some FJ-3s were later modified to control Regulus and F9F-6K Cougar target drones. In 1956 the Navy retro-fitted all its FJ-3s with probe-and-drogue air refueling equipment, a long probe being fitted under the left wing.
Variants
XFJ-2
Test and evaluation aircraft. Three built.
FJ-2 Fury
Single-seat fighter-bomber aircraft, equipped with folding wings; powered by one General Electric J47-GE-2 turbojet. 200 built.
FJ-3 Fury
Single-seat fighter-bomber version, powered by the more powerful 7,800 lbf (34.7 kN) Wright J65-W-2 or 7,650 lbf (34 kN) J65-W-4 turbojet engine. 538
built.
FJ-3M Fury
Improved version of the FJ-3, with the ability to carry AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missiles. 194 built.
FJ-3D
FJ-3D2
F-1C
MF-1C
DF-1C
DF-1D
Specifications (FJ-2)
Data from Combat Aircraft since 1945[1]
General characteristics
Crew: 1
Length: 37 ft 7 in (11.45 m)
Wingspan: 37 ft 1.5 in (11.31 m)
Height: 13 ft 7 in (4.14 m)
Wing area: 288 ft² (26.7 m²)
Empty weight: 11,802 lb (5,353 kg)
Max takeoff weight: 18,790 lb (8,523 kg)
Powerplant: 1× General Electric J47-GE-2 turbojet, 6,000 lbf (26.7 kN)
Performance
Maximum speed: 587 kts (1,088 km/h) at sea level
Range: 860 mi (1,593 km) (normal)
Service ceiling: 46,800 ft (14,300 m)
Rate of climb: 7,230 ft/min (2,204 m/s)
Armament
Guns: 4 × 20 mm (0.787 in) cannon
Related development
FJ-1 Fury
F-86 Sabre
FJ-4 Fury
Comparable aircraft
Dassault Mystère
F-9 Cougar
F-84F Thunderstreak
Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-15
Supermarine Swift
References
Notes
1. Wilson, Combat
Bibliography
Avery, Norm. North American Aircraft 1934-1998 Volume 1. Santa Ana, CA: Narkiewicz//Thompson, 1998. ISBN 0-913322-05-9.
Bowman, Martin. F-86 Sabre. London: Airlife, 2004. ISBN-1-84037-411-X.
Dorr, Robert F. "Fury: The Navy's Sabre." Air International, January 1993.
Dorr, Robert F. "North American FJ Fury." Aeroplane Monthly, February 2006.
Taylor, John, W.R., ed. Jane's All the World's Aircraft 1965-1966. London: Jane's All the World's Aircraft, 1967. ISBN 0-71061-377-6.
Wagner, Ray. The North American Sabre. London: Macdonald, 1963. No ISBN.
Wilson, Stewart. Combat Aircraft since 1945. Fyshwick, ACT, Australia: Aerospace Publications Pty Ltd, 2000. ISBN 1-875671-50-1.
Wilson, Stewart F-86 Sabre / MiG-15 Fagot / Hawker Hunter, Aerospace Publications Pty Ltd, 1995. ISBN 1-875671-12-9.
Winchester, Jim, ed. "North American FJ Fury." Military Aircraft of the Cold War (The Aviation Factfile). London: Grange Books plc, 2006. ISBN
1-84013-929-3.
Living Warbirds: The best warbirds DVD series.
Source: WikiPedia